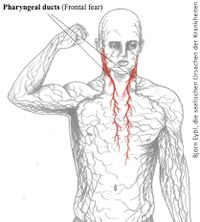
Pharyngeal ducts
Pharyngeal ducts are the remnants of the ancient gills necessary for life in water. During the embryological development of any mammal, there is the so-called "fish stage," in which the pharyngeal ducts can be clearly seen. Study of the CT scan revealed that Non-Hodgkin in not a program of the lymph nodes but in the ducts of the pharynx.
Location of impact, i.e. on which side the symptoms occur in the healing phase, depends on gender, biological laterality and hormone status. This is similar to the way the impact occurs in the territory, see also ectoderm.
Learn more about this in the online workshop "Bio-logical Behavior and Character".
Also see the general program of the ectoderm, thyroid ducts and lymph nodes.
Sensitivity follows the gullet mucosa pattern.
Theme
Frontal fear. Something is coming, someone does everything to avoid it, but it is impossible.
For example, bankruptcy, a partner's fatal illness.
CA phase
Functional increase. Decrease of cells in the mucous membrane of the pharyngeal ducts.
Biological purpose
Thinner mucous membranes so more water can flow through and thus more oxygen can be absorbed by the gills. Old, archaic program, it has lost its usefulness.
Symptoms
Sensitive, mild pain.
PCL phase
Functional normalization. Reconstruction of the mucous membranes of the pharyngeal ducts.
Symptoms
Non Hodgkin lymphoma. Swelling on the side of the neck, not painful. Much larger with the syndrome, may then be sensitive.
EC
Sensitivity, pain.