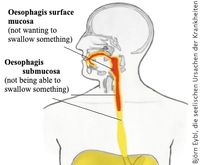
Esophagus, lower 1/3rd part
Also see: oral submucosa, nasal and pharyngeal submucosa, oral and pharyngeal surface mucosa.
Theme
Not being able to swallow a (food) morsel (right), i.e. wanting to swallow something but not being able or allowed to. Often it concerns a house or car or something similar, the purchase of which is unexpectedly cancelled, for example.
The upper 2/3 of the oesophagus is lined with squamous epithelium of the ectoderm: the oesophageal surface mucosa. In this case it is something that is forced upon you, it is forced down your throat against your will. So you prefer to spit it out, get rid of it.
CA phase
Functional increase, cell increase of esophageal submucosa for better digestion.
Biological purpose
To better to swallow the food morsel, better to digest.
- Cells of secretory quality: better digestion of the morsel due to cauliflower-like tissue growth for the production of more digestive juices.
- Cells of resorptive quality: bering able to better control and absorb the content of the morsel. Flat tissue growth.
Symptoms
None, with prolonged or intense conflict possible narrowing of the esophagus due to tissue growth of the secretory type, making swallowing difficult.
PCL phase
Functional normalization. Removal of extra cells by fungi or TB bacteria, if present.
Symptoms
Extreme fatigue and smelly night sweat, pain behind sternum, fever, smelly mouth. Due to healing swelling (more) difficulty swallowing solid food, gets much worse with the syndrome. Danger for undetected blood loss, watch for black stools!
In case of acute bleeding: surgery.
EC
Strong pain, giving up blood, chills.
Many relapses: enlarged and fused blood vessels in esophageal submucosa, blood vessel scar tissue.