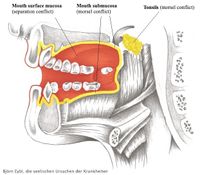
Mouth submucosa
Also see: mouth and pharyngeal surface mucosa, tonsils, salivary glands, salivary ducts
Themes
The submucosa of the mouth and palate share similar themes and are treated here together.
- Unable to get hold of a (food) morsel, unable to swallow. Wanting something but can't or shouldn't (right side). For example, someone receives notification that he has won the lottery but the ticket is in the wrong name.
- Not being able to spit out a morsel, i.e. getting something you don't want, you want to spit it out, vomit it out (left side). For example, your daughter is getting married to someone you don't trust.
Difference between left and right see ring shaped organism.
CA phase
Functional increase. Cell growth of the oral submucosa.
Biological purpose
- Better salivate the food morsel to improve swallowing. Result: morsel slides in more easily.
- Better salivate the food morsel to improve spitting it out. Result: chunk slips out more easily.
Symptoms
None, with intense conflict overproduction of saliva.
PCL phase
Functional normalization. Decomposition of extra cells by fungi or TB bacteria, if present.
Symptoms
Fatigue and/or night sweats, pain, smelly breath and foul taste in the mouth, possibly white or yellow rashes: thrush, leukoplakia, candidosis.