Smooth muscles of the intestines
Around the intestines are two layers of smooth muscle tissue: on the inside are the transverse muscles and on the outside are the longitudinal muscles.
Also see esophagus, small intestine, colon and rectum.
Theme
Motor aspect of an indigestible morsel, regarding the transportation of a morsel or food.
CA phase
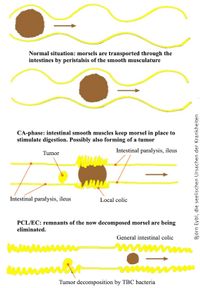
At the same time increase in function due to increase in muscle activity (peristalsis) and muscle tension in the part of the intestines where the morsel is located and loss of function (stop of peristalsis) in the rest of the intestines.
- Muscles at the level of the morsel "knead" it to stimulate digestion.
- Muscles in the rest of the intestine lie still to hold the morsel in place.
Biological purpose
Holding an kneading the morsel to stimulate digestion.
Symptoms
The part of the bowel where the lump is located shows enhanced muscle contractions while there are (almost) no muscle movements in the other parts. This is often diagnosed as paralyzed bowel or intestinal obstruction (Ileus).
PCL phase / EC
Slow down or stop of muscle activity in the part where the morsel was located and increased peristalsis in the rest of the intestines, intestinal colic. Subsequent normalization of muscle tension and peristalsis.
Hanging healing or many relapses: irritable bowel syndrome.
The complete intestinal program is shown in the figure below.