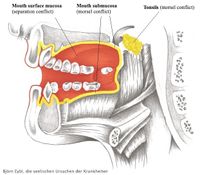
Tonsils
See also: mouth submucosa, mouth and pharyngeal surface mucosa, salivary glands, salivary ducts
Themes
- Unable to swallow a (food) morsel due to a lack of saliva (right tonsil), i.e. wanting to swallow something but not being able or allowed to. For example, a contract falls through at the last minute.
- Not being able to spit out (vomit) a morsel because of a lack of saliva (left tonsil), so getting something you don't want, you want to spit something out, vomit it out.
Difference between left and right see ring shaped organism.
CA phase
Functional increase. Cell increase in the tonsils.
Biological purpose
- To better salivate the morsel to swallow. Result: morsel slips in more easily.
- To better salivate the morsel to spit out. Result: chunk slips out more easily.
Symptoms
Enlarged tonsil(s).
PCL phase
Functional normalization. Decomposition of extra cells by fungi or TB bacteria, if present.
Symptoms
Tonsillitis, pussy tonsils. Fatigue and/or night sweats, smelly mouth, foul taste. Narrowing of pharynx due to healing swelling, extra strong with the syndrome: tonsil abscess.
Hanging healing or many relapses: shriveled almonds, "raisins."