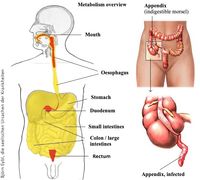
Appendix
The appendix is located just below the area where the small intestine empties into the large intestine and is a "dead end" so to speak.
Also see also: small intestines, colon, stomach.
Theme
Unpleasant, mean indigestible anger. For example, a child sees his parents attacking each other.
CA phase
Functional increase. Cell increase in the mucosa of the appendix.
Biological purpose
Better digest and/or absorb nutritional morsels.
- Cells of secretory quality: better digestion of food. Cauliflower-like tissue growth, polyps.
- Cells of resorptive quality: better absorption of the morsel or food. Flat tissue growth.
Symptoms
None.
PCL phase
Functional normalization. Removal of the extra cells by fungi or TB bacteria, if present.
Symptoms
Appendicitis. Fatigue, smelly night sweat, fever, possibly blood in stool.
The healing swelling can cause the appendix to snap: appendicitis perforation. For this, nature has found a perfect solution: the omentum (part of the peritoneum) folds itself over the rupture, preventing the spreading of the intestinal contents into the abdominal cavity and limiting the extent of the inflammation. This is considered a life-threatening peritonitis. With syndrome: abscess.
If perforation occurs, surgery is recommended.
EC
Chills, strength bleeding, colic, appendicitis perforation.
Allergies: celiac disease (gluten allergy) and cow's milk allergy. Gluten and milk proteins in cow's milk are traces.