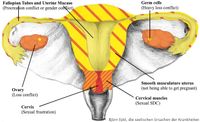
Ovaries
The ovary is the storage place of eggs and it produces estrogens, among other things. It is the female counterpart of the testicle.
Also see cervical muscles endometrium, fallopian tubes, cervical muscles and cervical mucosa.
Whether it is the left or right ovary depends on the biological laterality of the woman.
Theme
Tough loss conflict due to someone dying or leaving.
CA phase
Cell decrease, holes in the ovary, decrease in eustrogen production.
Symptoms
Usually undetected. Possible irregular menstruation, stop of menstruation and/or ovulation stop.
PCL phase
Rebuilding cells in the ovary.
Symptoms
Pain, swelling of the ovary. From the cavities, one or more cysts are formed, which fill up with ovarian tissue: ovarian cancer.
With the syndrome: risk of endometriosis (bursting of the cysts, each cell forms a separate cyst in the abdominal cavity)
Biological purpose
Biological purpose at the end of PCL-B: enlarged ovary, ovarian cyst.
Permanently increased production of eustrogen. This has a rejuvenating effect, delaying menopause and enhanced ovulation to replace what is lost as soon as possible. Increased estrogen production causes the woman to look years younger within a short period of time at the end of PCL-B.
So an ovarian cyst can occur in the PCL but it can also be the end stage.
Both ovaries (constellation): sexual megalomania, also see new mesoderm.