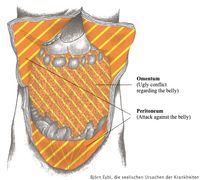
Peritoneum
There are many organs in the abdomen. These must be taken into account to determine the correct program.
Also see omentum.
Whether it is the left or right side of the peritoneum depends on biological laterality.
Theme
Attack against the abdomen, real (e.g., a knife wound) or metaphorical (e.g., a diagnosis: you have ovary cancer).
CA phase
Cell increase in the peritoneum. This can be flat growing: the entire abdomen is attacked or a cauliflower-like growth: a local attack. If the latter is the case, it is interpreted as a metastasis. This occurs mainly in the healing phase.
Biological purpose
Reinforcement of the peritoneum to better withstand the attack.
Symptoms
None.
PCL phase
Functional normalization. Removal of cells by TB bacteria, if present.
Symptoms
Peritonitis. Fatigue, night sweats, pain in the abdomen, possibly temperature elevation/fever. Fluid in the abdomen due to healing swelling. The fluid prevents the organs in the abdominal cavity from sticking together and form intestinal blockages. The organs "float" in the water.
With the syndrome: ascites. This causes many complaints: breathing problems, pain, discomfort, one feels the abdomen with every movement, with every breath.
The existence conflict will have to be resolved in order for someone to get out of this vicious circle. The ascites will then decrease drastically, 50% or more. Punctation can give some relief, but in practice it lasts only a very short time and subsequently more fluid is retained.
EC
Strong pains, chills and cold sweats.
There may be calcium deposits visible at the end of the PCL-B, see old mesoderm.